1. Reuse objects
- Rather than creating new objects that does the same job every time, reuse the single object by using static factory methods or immutable object.
- For example, use
Boolean.valueOf(String)which is a static factory method rather thanBoolean(String).
- Immutable objects like String can be reused any time. For example, use
String s = "bikini";rather thanString s = new String("bikini");
- For example, use
- Reuse the expensive object by caching

String.matches()can degrade the performance as it usesPatterninstance just once and discards it which leaves it to the GC.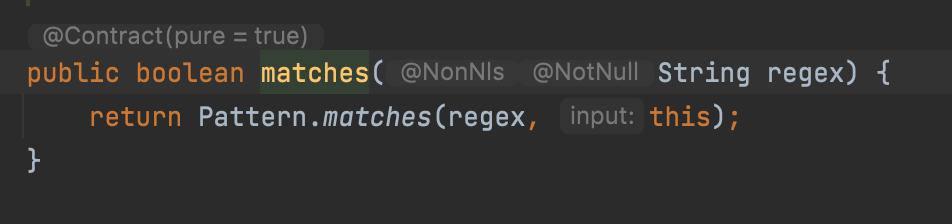
- To improve the performance, create the
Patterninstance from the class instantiating level by declaring it asstatic, and reuse whenever it’s required.
2. Adapter pattern
- Adapter is an object that delegates to a backing object, providing an alternative interface
keySet()ofMapinterface returns aSetview of theMapobject, which returns the sameSetinstance per every call.
3. Prefer primitives to boxed primitives

sum += i; would createLonginstance every time. Changing the sum type fromLongtolongimproves the performance much better.Long sum, long i=>
long sum, long i=>
Long sum,Long i=>
Check List
1. What is the difference between primitive type and boxed primitive type ?
- To Be Updated

Leave a comment